What Is Resonant Breathing & How To Use It For Calm and Wellness

Resonant breathing is a slow, steady breathing pattern. You breathe about 5 to 6 times per minute. Inhales and exhales are the same length. The rhythm tells your nervous system there is no threat, so your heart rate can slow and your muscles can relax. People use it when stress, tension, or racing thoughts build.
Slow, steady breaths activate the parasympathetic nervous system, the body’s rest and recovery mode. That lowers stress hormones and reduces tight, jittery sensations in your chest and stomach. Your breathing becomes a simple signal that calms the body.
Resonant breathing also improves heart rate variability, or HRV. HRV measures tiny timing changes between heartbeats. Higher HRV usually means your body handles stress better and recovers faster.
Because of these effects, practitioners use resonant breathing for anxiety, sleep, athletic recovery, and focus. Below you will find a clear explanation of how it works, step-by-step practice instructions, and simple ways to add it to your day.
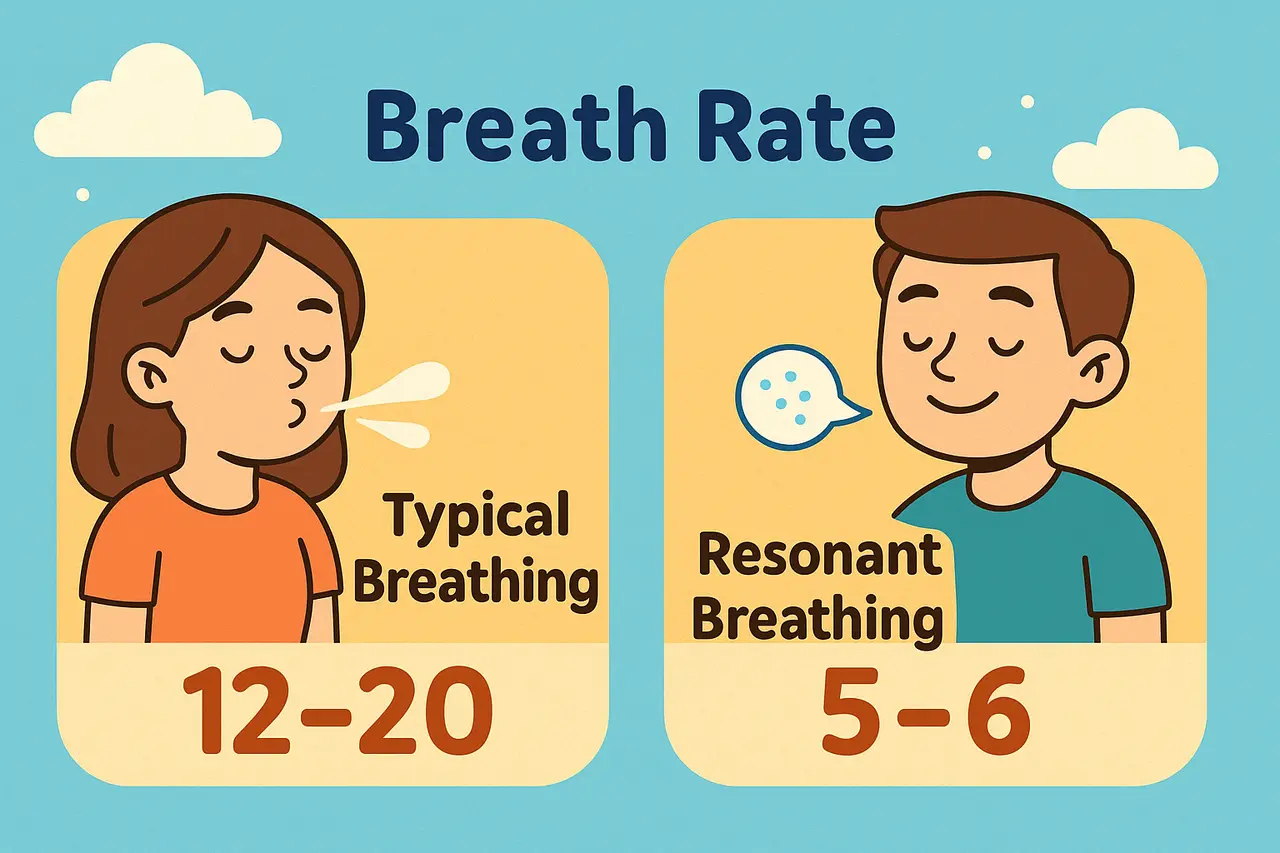
What Is Resonant Breathing?
Resonant breathing increases heart rate variability, which is a sign of a flexible and healthy nervous system. Studies link this pattern to better emotional control, lower anxiety, and improved cardiovascular function.
When you breathe at this rhythm, your heart rate gently rises on the inhale and falls on the exhale, which strengthens the baroreflex, the system that helps regulate blood pressure.
According to the journal Frontiers in Public Health, breathing at your personal resonance frequency, usually near 6 breaths per minute, can significantly improve heart rate variability and support emotional well‑being.
How to practice resonant breathing
Use this simple structure to get started. You can practice sitting or lying down.
Safety and tips
Most healthy people can practice resonant breathing safely, but anyone with serious heart, lung, or blood pressure conditions should check with a healthcare professional first.
If you feel dizzy, short of breath, or uncomfortable, return to your normal breathing and rest. Over time, this practice often feels natural and can become a simple daily tool to steady your mind and body.
Note: Resonant breathing isn’t about taking big breaths. It’s about finding a steady comfortable pattern that relaxes your mind and body.

Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and Resonant Breathing
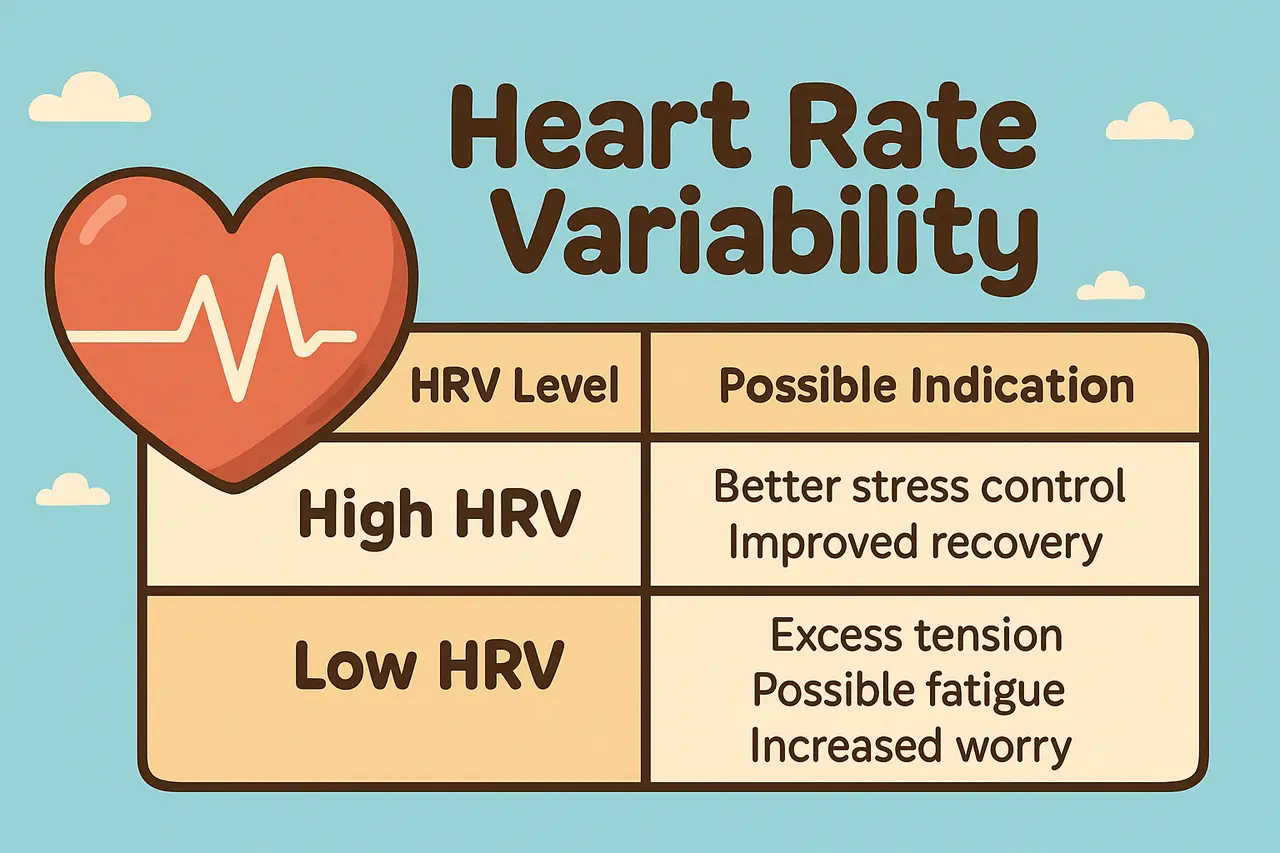
Heart rate variability (HRV) measures the changes in time between heartbeats. High HRV shows the body adapts well to challenges. Low HRV may indicate higher stress.
Resonant breathing may improve HRV by slowing each breath. This steady rhythm helps the heart and lungs work together smoothly.
The autonomic nervous system has two parts. The sympathetic system triggers a stress response. The parasympathetic system promotes rest. Resonant breathing activates the parasympathetic system to help the body relax.
This process can calm stress hormones and relax tense muscles. It also promotes emotional stability and sharper thinking.
Below is a basic overview of how HRV is measured and what it can indicate:
You can measure HRV with wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers. These devices track your heart rate and display HRV data. These devices offer real-time feedback.
This helps you see how activities, like resonant breathing, influence your HRV. Apps for HRV tracking can guide you through ways to improve it. They often include slow breathing exercises to help.
Research shows that resonant breathing may help the vagus nerve. This nerve controls heart rate and digestion. When the vagus nerve is more active, the body tends to relax.
This makes resonant breathing a friendly tool for those looking to manage tension and boost long-term wellness.
Some research suggests that this gentle breathing technique may also support the vagus nerve, which influences heart rate and digestion.
When the vagus nerve is more active, the body tends to relax. This makes resonant breathing a friendly tool for those looking to manage tension and boost long-term wellness.
The Vagus Nerve and Stress Response
The vagus nerve connects the brainstem to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. When this nerve is more active, it helps your body slow down and recover from everyday pressures.

How Resonant Breathing Supports the Vagus Nerve
Resonant breathing can gently support vagus nerve activity by guiding your heart rate into a calmer pattern. One way to understand this is to think of the vagus nerve as a communication bridge between your mind and body.
When you breathe at about five to six breaths per minute, you send signals of safety to the brain. These signals encourage the release of fewer stress hormones and increase parasympathetic activity, which further settles the body.
Quick Facts About the Vagus Nerve:
Benefits of Consistency
Many find that consistent practice of resonant breathing over time leads to fewer episodes of racing thoughts or worry. By harnessing this gentle rhythm, you may notice improvements in how quickly you can calm yourself during hectic moments. This makes it a helpful tool for general wellness.
Physical and Emotional Benefits of Resonant Breathing
Coherent breathing goes beyond just slowing your breath. Many people find it brings calm to both body and mind. By keeping a steady pace of about five or six breaths per minute, heart rate variability (HRV) coherence often improves. This can help reduce overall tension, sharpen focus, and create a more stable mood.
Possible Benefits of Resonant Breathing:
A case study published in a wellness journal showed that participants who practiced coherent breathing for a few weeks reported steadier energy and fewer anxious thoughts. Some even noted less emotional reactivity during hectic periods.
While results vary from person to person, these findings suggest that regular practice can be a simple yet useful step toward better physical and mental health.

How to Practice Resonant Breathing
Resonant breathing can be started with a few easy steps. Find a quiet spot where you feel secure, whether on a sofa or a yoga mat. Then, follow a calm pattern of inhaling and exhaling that sums to roughly five or six breaths per minute.
Step-by-Step Guide
Some people use breathing apps like Breathe+ or Calm to guide their pace with visual or sound cues. Others picture air flowing in harmony with their heartbeat. Choose a soothing pace that feels natural, not forced. With practice, this rhythm becomes easier.
Subscribe to Create Higher Vibrations!
Get Inspiration and Practical advice straight to your inbox.
Resonant Breathing in Daily Life
Resonant breathing can become part of your routine in simple ways. Many people add it to their morning habits, while others prefer using it before bedtime to settle the mind. You can also pause at work or during study breaks to take a few slow breaths and refocus.
Suggestions for Daily Integration:
Some find that writing short reminders on sticky notes or setting phone alerts helps make this a consistent habit. Over time, these small moments of calm may lead to lower stress, steadier emotions, and stronger mental focus.
Final Thoughts
Hrv Resonant breathing stands out as a gentle, steady method that helps center both mind and body. By focusing on a pace of five or six breaths each minute, the heart and lungs align their rhythms in a way that eases tension.
This practice offers many benefits. It helps manage stress and enhances cognitive function. It supports cardiovascular wellness, promotes emotional balance, and improves sleep quality. Many find it acts like a bridge to calmness, as it triggers the parasympathetic system to encourage relaxation.
If you’re new to this technique, start slowly. Find a comfortable breathing count and integrate it into daily habits. When paired with yoga, walks in nature, or simply a moment of stillness before bedtime, resonant breathing can serve as a reliable companion.
Regular practice can reduce rushing thoughts, steady your mood, and bring relaxation. Even brief sessions can improve well-being and offer an easy way to care for yourself.


