The Power of Perception: How to Change Your Reality

You buy a specific car model. Suddenly, you see that car everywhere.
It was always there. You just never noticed it before.
This is the power of perception in action. Your brain does not record reality like a camera. It constructs reality like an artist. It picks and chooses what to show you based on what you believe.
This process shapes your relationships. It dictates your success. It controls your happiness.
If you change your perception, you change your entire life experience.
Here is the psychology behind how we see the world and how to master it.
- Perception builds reality. It is an active interpretation of events, not a passive recording of facts.
- Your brain filters the world. The Reticular Activating System (RAS) only admits data that matches your current beliefs.
- Biases distort the truth. Mental shortcuts like Confirmation Bias trap you in old, repetitive narratives.
- You can rewrite the story. Pause your reaction, challenge your assumptions, and assign a new, empowering meaning.
What Is Perception in Psychology?
Many people use “sensation” and “perception” interchangeably. They are not the same thing.
Sensation is the raw data. It is light hitting your retina. It is sound waves hitting your eardrum. It is purely physical.
Perception is what your brain does with that data. It is the story you tell yourself about what you just saw or heard.
Perception is the process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory information.
Sensation vs. Perception: The Critical Difference
Imagine you are sitting in a coffee shop.
The noise was the same. The reality was the same. Your internal experience was completely different. The power of perception lies in that gap between the stimulus and your response.

The 3 Stages of Perception
Psychologists break this process down into three distinct steps.
The Biology of Belief: Your Reticular Activating System (RAS)
You might think you see reality clearly. You do not.
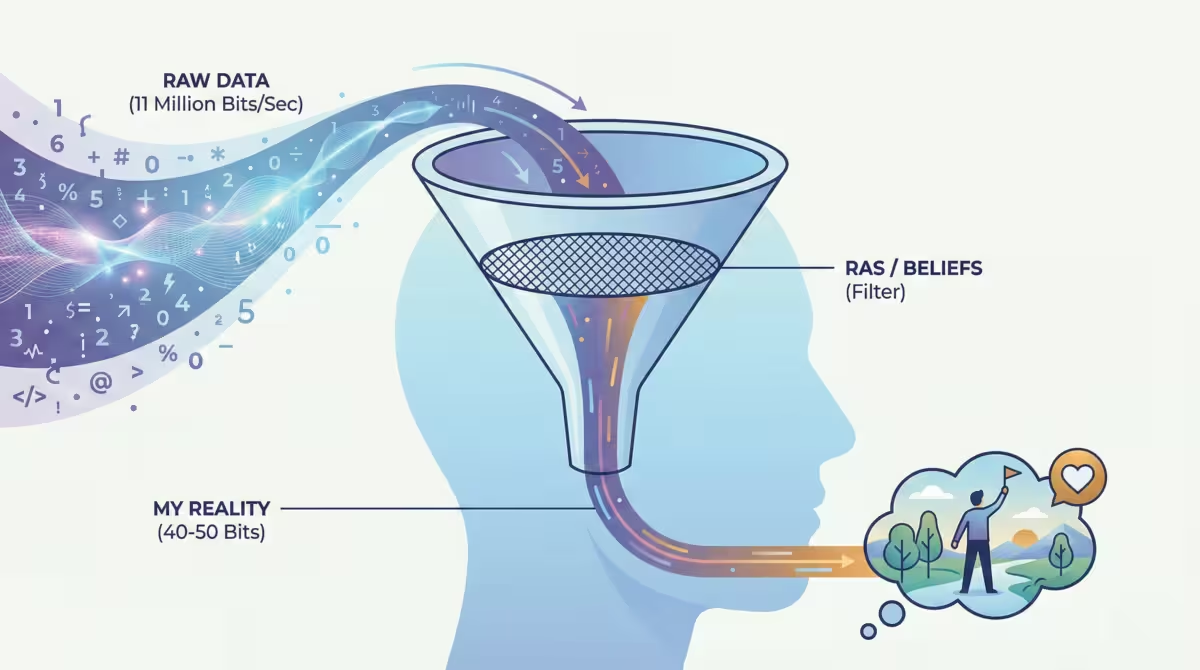
Your brain processes millions of bits of data every second. If you paid attention to all of it, you would go insane. You need a filter.
That filter is the Reticular Activating System (RAS).
How Your Brain Filters 99% of Reality
The RAS is a bundle of nerves at your brainstem. It acts like a nightclub bouncer for your brain.
It decides what information gets in and what stays out.
The bouncer has a strict guest list. That list comprises your beliefs, your fears, and your goals.
If you believe “people are generally mean,” your RAS lets in evidence of rudeness. It blocks out the person holding the door for you. You literally do not see the kindness. It does not fit the guest list.

Why You See What You Expect to See
This is why two people can watch the same news broadcast and see two different realities. Psychologists often refer to this frequency illusion as the Baader-Meinhof phenomenon.
Their RAS filters are set to different frequencies.
This biological function proves a spiritual truth: You do not see the world as it is. You see the world as you are.
The “Perceptual Set” and Cognitive Biases
Your RAS creates a “Perceptual Set.” This is a tendency to notice only certain aspects of a situation.
This leads to cognitive biases. These are mental shortcuts that distort reality.
Confirmation Bias (The Echo Chamber)
This is the most common error. You favor information that confirms what you already believe.
If you think you are unlovable, you will fixate on a text message that takes two hours to arrive. You will ignore the three friends who called you yesterday. You are building a case against yourself.
The Halo Effect
This occurs when one positive trait colors your view of a person’s entire character.
We often assume good-looking people are also smart, funny, and kind. We let our initial positive perception blind us to red flags. This is common in the honeymoon phase of relationships.
Subscribe to Create Higher Vibrations!
Get Inspiration and Practical advice straight to your inbox.
Fundamental Attribution Error
We judge others by their actions, but we judge ourselves by our intent.
Recognizing this bias instantly lowers your anger levels.
Perception vs. Reality: A Practical Comparison
We often suffer more in our imagination than in reality.
The event is neutral. The perception creates the emotion.
| The Event (Neutral Fact) | Perception A (Limited) | The Consequence | Perception B (Empowered) | The Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Your boss asks for a meeting. | “I am in trouble. I messed up.” | Anxiety, defensiveness. | “They want my input on a project.” | Curiosity, confidence. |
| It rains on your vacation. | “My trip is ruined. Just my luck.” | Anger, disappointment. | “I can finally read my book and rest.” | Relaxation, peace. |
| A friend cancels plans. | “They don’t respect my time.” | Resentment. | “They must be overwhelmed.” | Compassion. |
“I once worked with a client who believed her team hated her. We tracked her interactions for a week. She realized she was misinterpreting neutral silence as disapproval. Once she shifted that lens, her leadership scores doubled.”
How to Shift Your Perception (5 Actionable Steps)
You cannot control every event. You can control how you decode it.
Perception is the foundation of emotional intelligence because you cannot manage an emotion until you understand the story that created it. Follow these steps to change your view.
Step 1: Pause and Label the Story
The moment you feel a strong emotion, hit the pause button.
Separate the fact from the fiction.
Ask yourself: “What is the raw data, and what is the story I added?”
Step 2: Challenge the Narrative
Do not believe your first thought. Your brain is lazy. It uses old paths.
Ask these questions:
Step 3: The “Camera Lens” Technique
Zoom out. Imagine you are a director filming this scene. By viewing the scene as a director, you remove the ‘me’ from the equation and stop taking the interaction personally.
View the situation from a third-party perspective.
If a stranger saw this interaction, what would they see? They would likely see two tired people miscommunicating. They would not see a villain and a victim.
Step 4: Regulate the Nervous System
You cannot perceive clearly when you are in “fight or flight” mode.
When you are stressed, your focus narrows. You only see threats.
Take five deep breaths. Signal to your body that you are safe. A calm nervous system widens your perception. It allows you to see options and solutions.
Step 5: Assign a New Meaning
You are the author of your reality. You get to decide what things mean.
This is not about “toxic positivity.” It is about utility.
Ask: “How can I view this in a way that helps me move forward?”
The traffic jam is not a punishment. It is a chance to listen to a podcast. The rejection is not a failure. It is a redirection.
Discover Your Inner Self. Join Our Self-Mastery Program.
Self-Mastery Coaching gives you the space, tools, and guidance to grow, reflect and discover your values and inner strength.

Higher Consciousness: The Spiritual Aspect of Perception
Psychology calls it “reframing.” Spirituality calls it “awakening.”
In many spiritual traditions, the goal is to cleanse the doors of perception. We aim to remove the filters of ego and fear.
When you master the power of perception, you stop reacting to life. You start creating it.
You realize that the world “out there” is a reflection of the world “in here.”
Final Thoughts
You are not a passive observer of your life; you are its creator.
Every moment offers you a choice. You can let your old patterns dictate your emotions, or you can pause and choose a new perspective.
This shift does not happen overnight. It requires practice. But the reward is worth the effort: a life defined not by what happens to you, but by how you choose to see it.
Start today. Challenge one narrative. Question one reaction.
Change your perception, and you will change your world.


